
Pyspark invokes the more general spark-submit script. bin/pyspark -master local -py-files code.pyįor a complete list of options, run pyspark -help. Or, to also add code.py to the search path (in order to later be able to import code), use: $. For example, to runīin/pyspark on exactly four cores, use: $. You can also add dependenciesĬan be passed to the -repositories argument. To the runtime path by passing a comma-separated list to -py-files. In the PySpark shell, a special interpreter-aware SparkContext is already created for you, in theĬontext connects to using the -master argument, and you can add Python. Spark-shell invokes the more general spark-submit script. bin/spark-shell -master local -packages "org.example:example:0.1"įor a complete list of options, run spark-shell -help. To include a dependency using Maven coordinates: $. bin/spark-shell -master local -jars code.jar Or, to also add code.jar to its classpath, use: $. For example, to run bin/spark-shell on exactlyįour cores, use: $. Sonatype)Ĭan be passed to the -repositories argument. Any additional repositories where dependencies might exist (e.g. Spark Packages) to your shell session by supplying a comma-separated list of Maven coordinates You can set which master theĬontext connects to using the -master argument, and you can add JARs to the classpathīy passing a comma-separated list to the -jars argument. Making your own SparkContext will not work. In the Spark shell, a special interpreter-aware SparkContext is already created for you, in the $ PYSPARK_PYTHON =/path-to-your-pypy/pypy bin/spark-submit examples/src/main/python/pi.py Initializing Spark You can specify which version of Python you want to use by PYSPARK_PYTHON, for example: $ PYSPARK_PYTHON =python3.8 bin/pyspark It uses the default python version in PATH,
#ELEMENT SYNONYM DRIVER#
PySpark requires the same minor version of Python in both driver and workers.

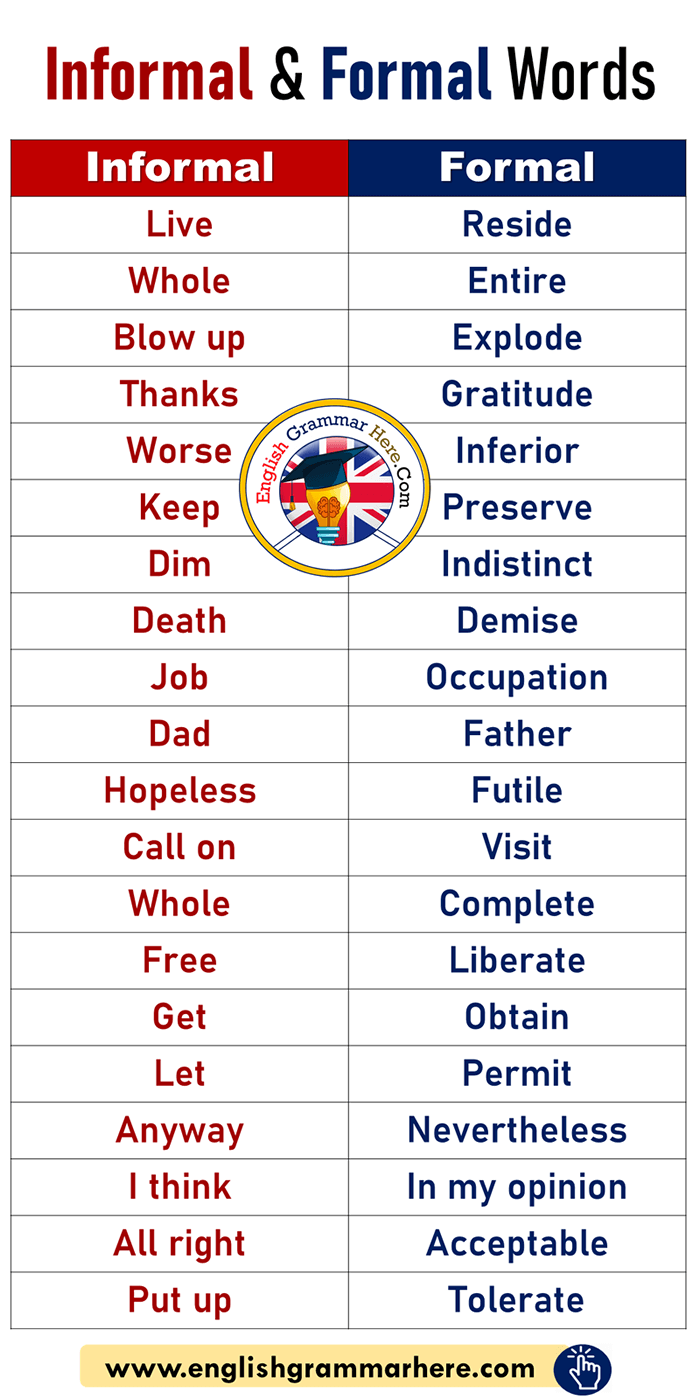
Add the following line: from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConf Prebuilt packages are also available on the Spark homepageįinally, you need to import some Spark classes into your program. If you wish to access HDFS data, you need to use a build of PySpark linking You can also use bin/pyspark to launch an interactive Python shell. This script will load Spark’s Java/Scala libraries and allow you to submit applications to a cluster. To run Spark applications in Python without pip installing PySpark, use the bin/spark-submit script located in the Spark directory. Spark applications in Python can either be run with the bin/spark-submit script which includes Spark at runtime, or by including it in your setup.py as: install_requires = Python 3.6 support was removed in Spark 3.3.0. Python 2, 3.4 and 3.5 supports were removed in Spark 3.1.0. It can use the standard CPython interpreter, It is easiest to followĪlong with if you launch Spark’s interactive shell – either bin/spark-shell for the Scala shell orīin/pyspark for the Python one. This guide shows each of these features in each of Spark’s supported languages. Spark supports two types of shared variables: broadcast variables, which can be used to cache a value in memory on all nodes, and accumulators, which are variables that are only “added” to, such as counters and sums. Sometimes, a variable needs to be shared across tasks, or between tasks and the driver program. By default, when Spark runs a function in parallel as a set of tasks on different nodes, it ships a copy of each variable used in the function to each task. Finally, RDDs automatically recover from node failures.Ī second abstraction in Spark is shared variables that can be used in parallel operations. Users may also ask Spark to persist an RDD in memory, allowing it to be reused efficiently across parallel operations. RDDs are created by starting with a file in the Hadoop file system (or any other Hadoop-supported file system), or an existing Scala collection in the driver program, and transforming it. The main abstraction Spark provides is a resilient distributed dataset (RDD), which is a collection of elements partitioned across the nodes of the cluster that can be operated on in parallel. At a high level, every Spark application consists of a driver program that runs the user’s main function and executes various parallel operations on a cluster.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
